Stable isotope analysis in medical and biochemistry research
Understanding of the biological processes that control human and animal physiology plays an important role in medical and biochemistry research. These disciplines make use of stable isotope analysis through non-invasive labeling techniques to provide information on biochemical reactions or metabolic pathways within the body, e.g. by breath analysis. The use of enriched isotope tracers with artificially high abundances of minor isotopes provides a relatively simple way of probing subtle biological processes.
Breath analysis
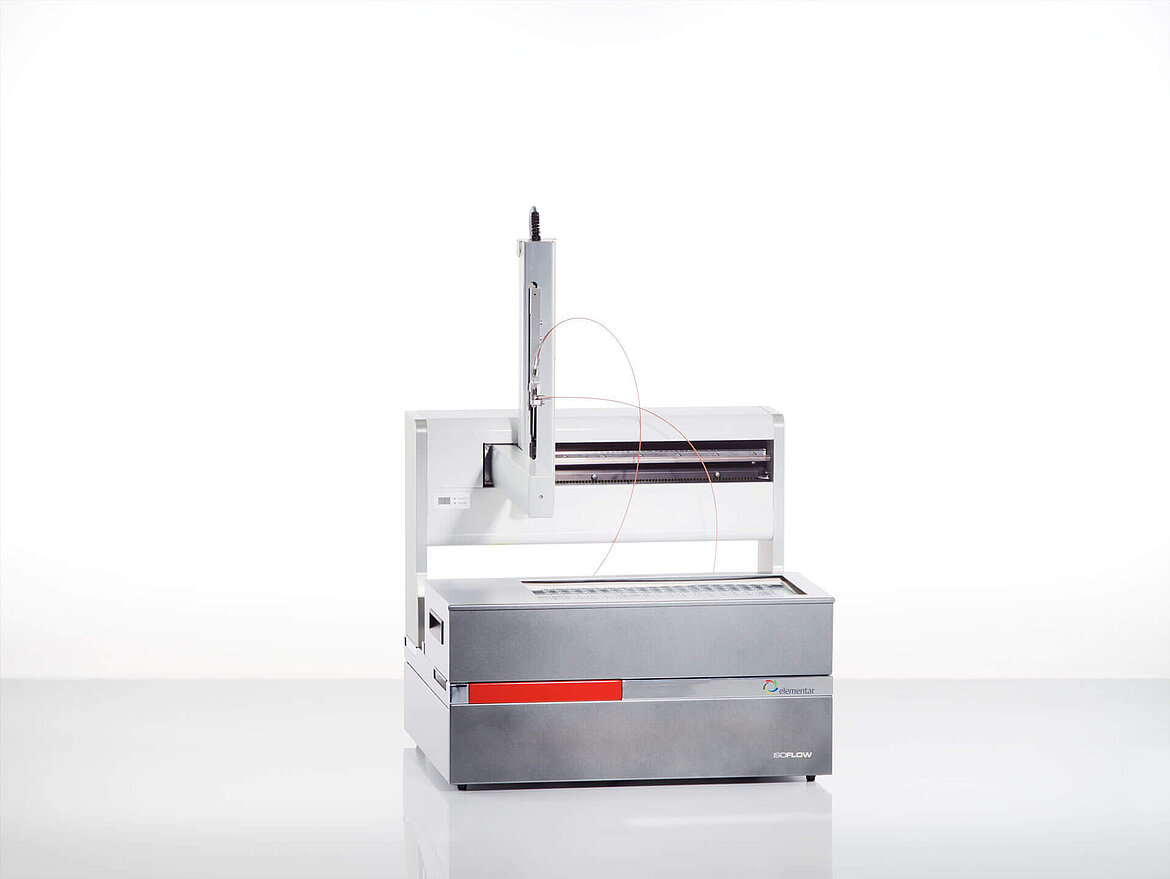
Breath analysis using stable isotope analysis allows the non-invasive determination of whole-body CO2 production. After your subject has ingested an isotopically labeled meal (e.g. 13C-labeled glucose), breath analysis will show that exhaled CO2 from the patient shows enrichment in 13C levels relative to 12C. The time taken for the 13C isotope to appear in the exhaled breath gives some indication of the metabolic rate of the subject. Up to 220 breath samples can be analyzed using our iso FLOW sample handling system for rapid analysis of large numbers of samples.
Body fluid analysis
Dosing a subject (human or animal) with doubly labeled water (e.g. water enriched in both deuterium and 18O) allows the total energy expenditure (TEE) of the subject to be determined. High performance deuterium and 18O isotope analysis of up to 180 saliva, blood, and urine samples can be performed via headspace equilibration using the iso FLOW sample handling system.
Biochemical analysis
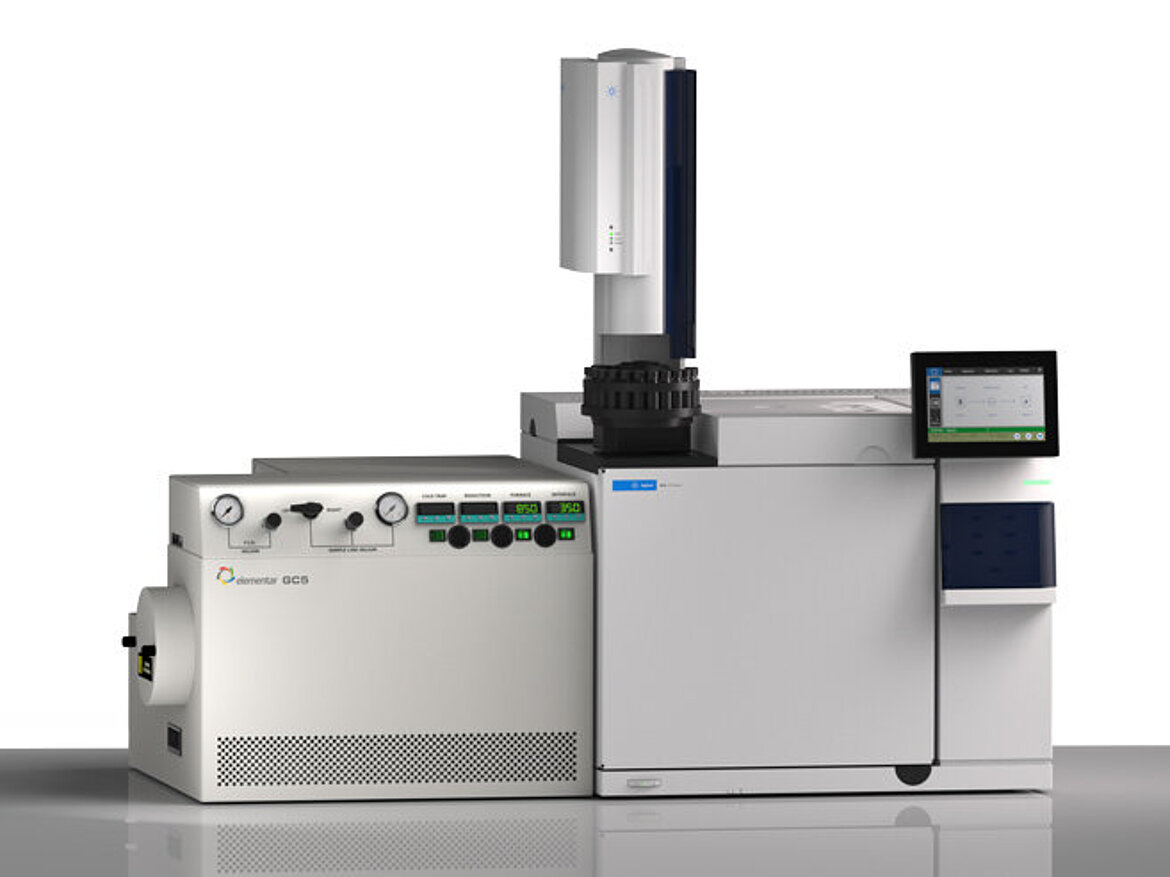
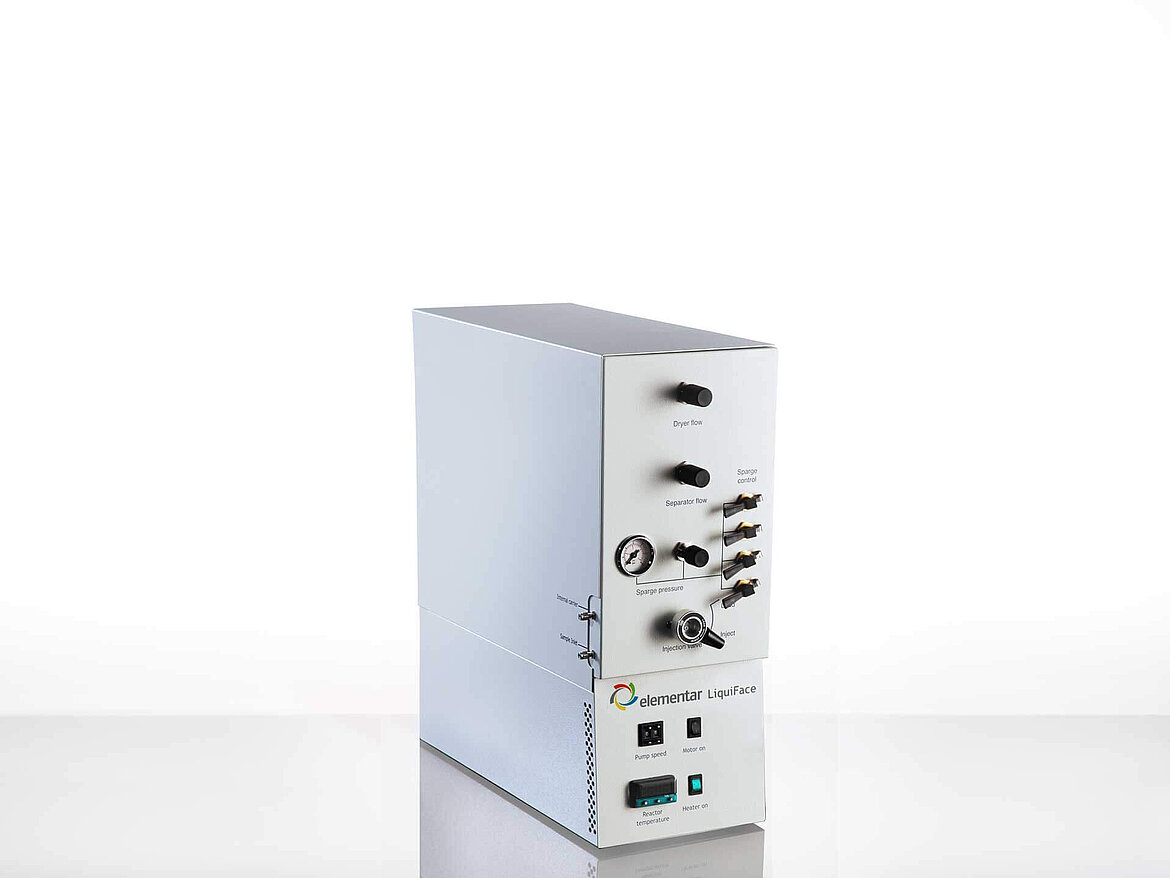
To understand more about the complex physiological chemical processes that occur within the body, it is necessary to go beyond coarse breath analysis and body fluid analysis. Our gas and liquid chromatography (GC-IRMS and LC-IRMS) systems are able to perform individual compound stable isotope analysis allowing you to find out more about these complex processes.